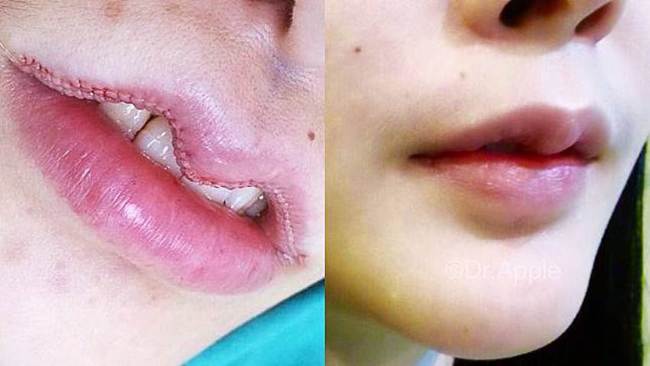
Each year, it is estimated that around 100 million people in developed countries acquire scars after undergoing elective surgery and surgery for trauma. In a purely cosmetic surgical procedure such as an aesthetic breast surgery, scarring is viewed as a source of dissatisfaction among patients.
Prevention and treatment of unaesthetic scar formation after an operation greatly rests on plastic surgeons who perform these operations. Scarring may have several unpleasant aesthetic and psychological consequences to the patients including diminished self esteem, stigmatization, anxiety and depression.
In a study published at Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive & Aesthetic Surgery, an international, multidisciplinary group of 24 experts developed a set of practical, evidence-based guidelines for the management of linear, hypertrophic and keloid scars which could be useful for surgeons, dermatologists, general practitioners and other physicians involved in the prevention and the treatment of scars.
Here are some of the results:
1. After a surgery, prevention of abnormal scar formation should be a priority. In an elective surgery, the position and length of scar is to be greatly considered. As much as possible, the incision should be parallel to the relaxed skin tension lines. During the operation, the surgeon should ensure that excessive tension on the wound edges is avoided. Several measures may also be done to reduce inflammation, provide rapid wound closure, reduce the risk of infection, and provide an early surgical wound coverage.
2. Following a wound closure, scar prevention consists of three phases: tension relief, hydration/taping/occlusion, and pressure garments. Recent studies show that offloading mechanical forces using a stress-shielding device made from silicone polymer sheets and pressure-sensitive adhesive significantly reduced scar formation. Also, the use of botulinum toxin A decreases tensile forces on post-surgical scars and results in significant improvements in the cosmetic appearances of scars compared with placebo injections.
3. Silicone products may help to prevent excessive scar formation by restoring the water barrier through occlusion and hydration of the stratum corneum and need to be used as soon as the wound/suture is healed. Moisturizing emollient and humectant creams and moisture-retentive dressings such as silicone sheets and fluid silicone gel have been shown to be beneficial for itching scars, and can also reduce the size and pain or discomfort associated with scars as well as improving their appearance.
4. Randomized studies in animals and humans have shown that ultraviolet radiation increases scar pigmentation and worsens their clinical appearance. A preventive measure of avoiding exposure to sunlight and the continued use of sunscreens with a high to maximum sun protection factor (>50) until the scar has matured is recommended.
5. For patients with linear hypertrophic scars who have further scar maturation after 6 months, silicone therapy should be continued for as long as necessary. For those with an ongoing hypertrophy, more invasive measures are indicated such as the use of intralesional corticosteroids. This is the only invasive management option which currently has enough supporting evidence to be recommended in evidence-based guidelines.
Additional injectable treatment options which may help to treat hypertrophic scars (and keloids) include bleomycin, 5-fluorouracil and verapamil, although the evidence to support these is currently more limited than for intralesional corticosteroids. If the patient develops a permanent (>1 year) hypertrophic scar, surgical scar revision may be considered.
Pressure therapy has recently been considered as an ‘evidence-based’ modality for the treatment of scars. The mechanism of its action remains poorly understood despite its widespread use around the world. Part of the effect of pressure could involve reduction of oxygen tension in the wound through occlusion of small blood vessels resulting in a decrease of (myo)fibroblast proliferation and collagen synthesis. Pressure therapy can also provide symptomatic treatment benefits such as the alleviation of oedema, itchiness and pain which may contribute to the patient's well-being.
Laser therapy is another invasive option which can be used to treat the surface texture of abnormal scars and may also be suitable for the treatment of residual redness, telangiectasias or hyperpigmentation. This has also been advocated for the prevention or minimization of both post-surgical and traumatic scars, and even in combination with botulinum toxin. An increasing number of articles being published on the successful management of hypertrophic scars with lasers is increasing the interest in this therapeutic modality.
6. Keloids are also best treated in centres with specialized expertise. Patients with growing minor or major keloids should first be treated with silicones in combination with pressure therapy and intralesional injections of corticosteroids. Some experts recommend that the lateral parts of keloids should not be excised, but should be joined together and left in situ. However, others have objected to this proposal and consider that the cells from these lateral parts of the keloid are more active in terms of collagen production.
Both electron beam irradiation and brachytherapy with iridium 192 can be used after surgical removal of the keloid to reduce recurrence rates. Objections were raised because of the potential risk of inducing malignancy but a study conducted has concluded that the risk of malignancy attributable to keloid radiation therapy is minimal.
Cryotherapy may also be used as an invasive treatment modality for keloids. In a study of 10 patients, scar volume was significantly reduced by 54% after one intralesional treatment with no recurrence over an 18-month follow-up period.
7. Silicone therapy is advocated as a non-invasive first-line prophylactic and treatment option for both hypertrophic scars and keloids. For non-invasive scar management options. silicone sheets and silicone gels are universally considered as the gold standard in scar management and the only non-invasive preventive and therapeutic measure for which there is enough supporting data to make evidence-based recommendations.
Silicone therapy is easy to use and is associated with only minimal side effects such as pruritus, contact dermatitis and dry skin. This therapy is believed to prevent and treat scars through occlusion and subsequent hydration of the scar tissue. Several clinical studies have indicated the beneficial effects of silicone gels in the prevention and treatment of scars. Several comparative studies with silicone sheets have shown that fluid silicone gels have at least equivalent efficacy although patients may find the gel formulations easier to use.
Scars may leave several psychological impacts on patients after their surgery. It is important that appropriate scar management measures are done and tailored to the needs of the individual patient and wound requirement. Preventive measures should be prioritized and applied before, during, and after wound closure.
For more details, you may visit:
http://www.jprasurg.com/article/S1748-6815(14)00173-9/fulltext